AimGel™ 技术
一个模块化细胞调控平台。
仿生学设计
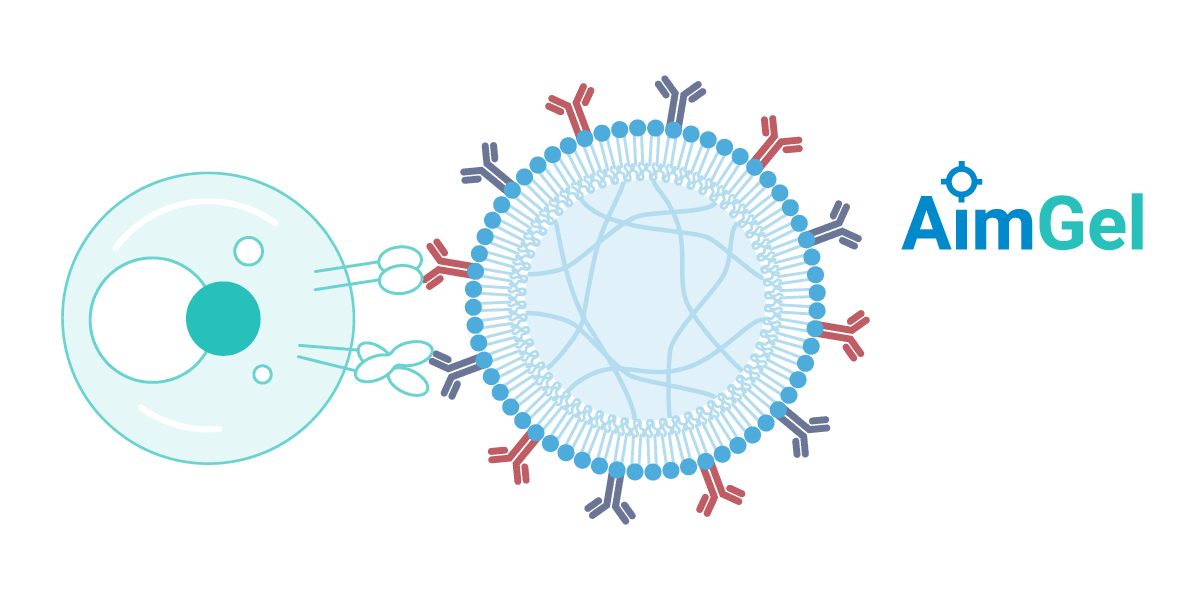
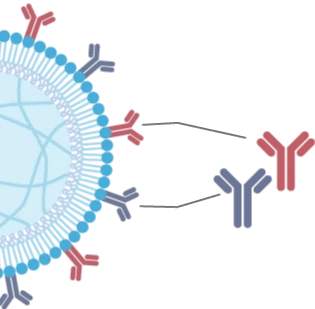
AimGel 人工细胞从底层设计之初就以模拟天然抗原呈递细胞(APC)为目标。其柔软的的水凝胶内核复刻了真实细胞的机械刚度与尺寸(约 10–15 微米),而可流动的脂质双层包被则让激活信号能够在表面自由移动——正如其在天然 APC 膜上的行为一样。
这一仿生设计带来了可量化的优势:与刚性的磁性微塑料珠相比,AimGel 所需激活信号显著更少,却能实现更高效且更温和的激活。最终表现为更高的细胞扩增率、更优的细胞活力和更低的耗竭水平——细胞始终保持响应能力,并可被再次刺激。
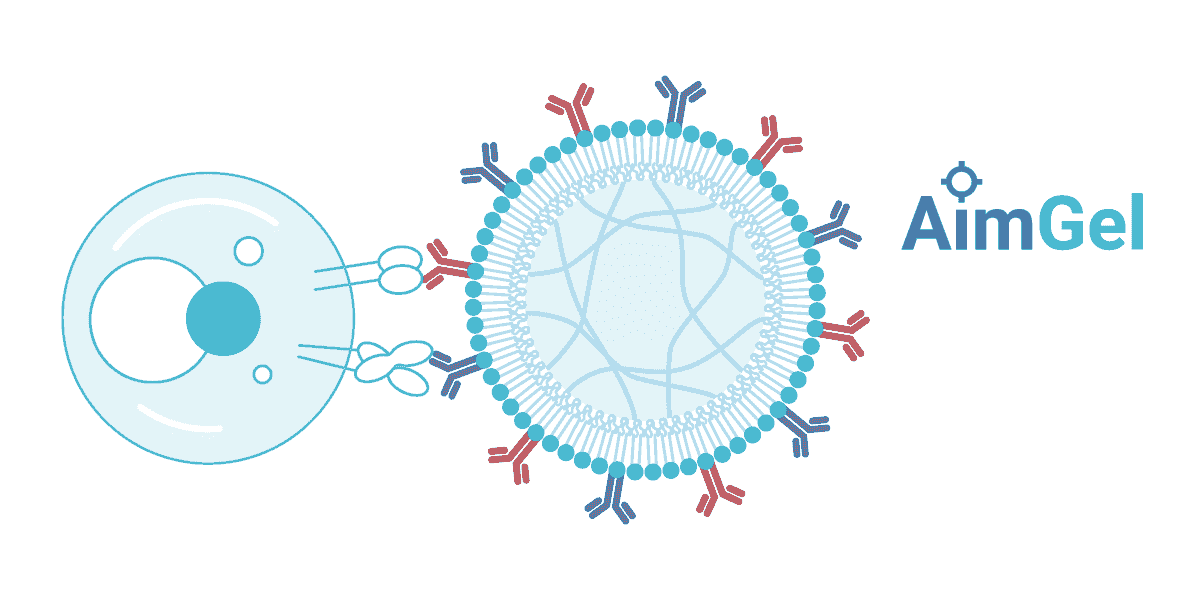
一个平台,无限应用
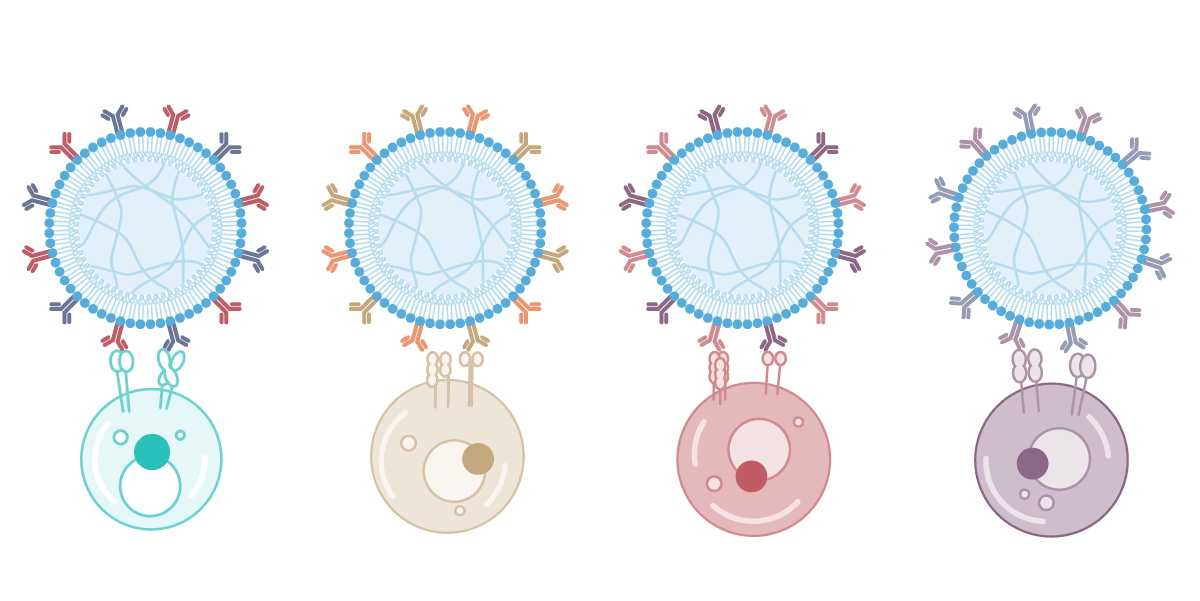
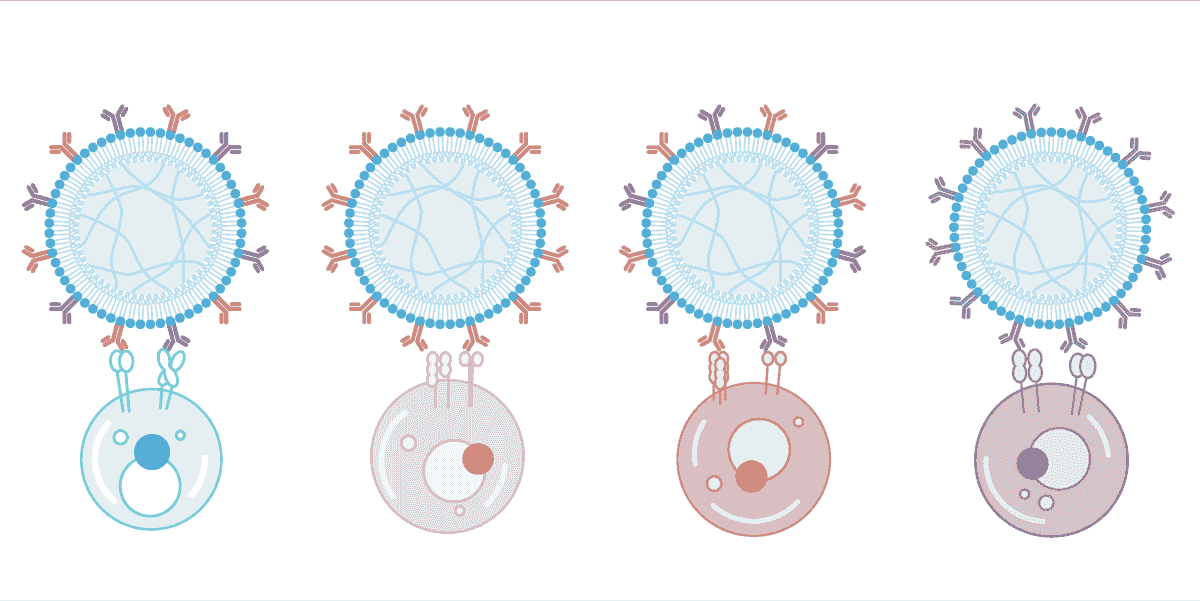
AimGel的核心优势在于其模块化设计。降解动力学、微珠尺寸和信号负载能力均可通过化学方法调控,使您能够精确控制激活参数。根据不同实验需求加载不同信号——目前已针对T细胞和NK细胞激活进行优化,Treg细胞解决方案即将推出。
该平台可适应您的研究需求:调整激活持续时间、协调慢病毒转导时机,或设计全新的信号组合。一个灵活的平台,为您特定应用量身配置。
明确的、一致的、合规的
AimGel 完全由合成物质构成,具有完全明确的结构和比例。不含任何动物成分,意味着批次之间不存在差异——每次实验都能获得稳定、可重复的激活效果,值得信赖。
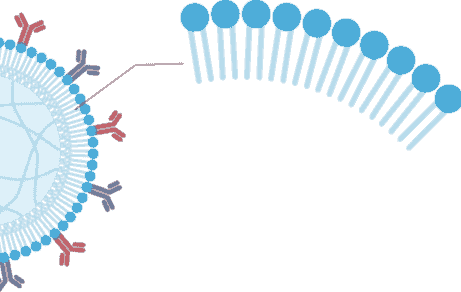
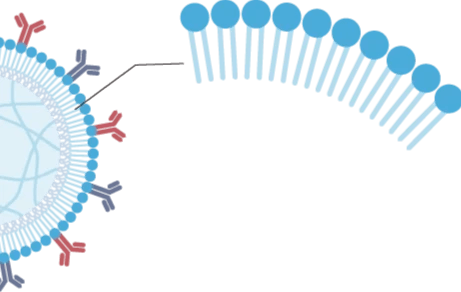
流动性膜
简一层类似细胞膜的流动脂质层能够实现类似细胞的相互作用。膜被改造以用于信号的附着。
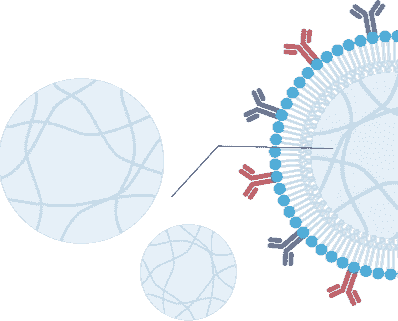
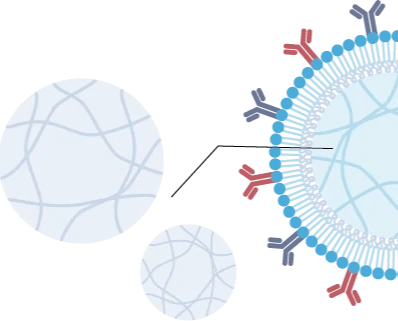
水凝胶核心
一个可降解的具有可变大小和柔软度的水凝胶核心,能够模拟真实细胞的质地。膜经过改造,可用于信号附着。
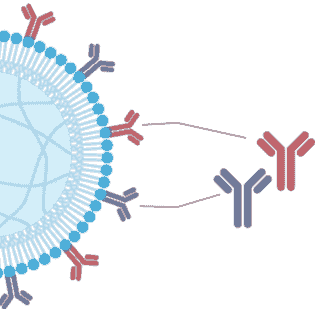
表面信号配比优化
易于更换,针对您所选的细胞类型进行了优化。
代表性技术论文
- Chung JT & Chau Y. (2023). Self-adjuvanted L-arginine modified dextran-based nanogel for sustained local antigenic protein delivery to antigen presenting cells and enhanced cellular and humoral immune responses. (under review)
- Chung JT, Lau CML, Chung CH, Rafiei M, Yao S & Chau Y. (2023). Vaccine delivery by zwitterionic polysaccharide-based hydrogel microparticles showing enhanced immunogenicity and suppressed foreign body responses. Biomaterials Science, 11(14), 4827-4844.
- Jahanmir G, Lau CML, Yu Y & Chau Y. (2022). Stochastic Lattice-Based Modeling of Macromolecule Release from Degradable Hydrogel. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 8(10), 4402-4412.
- Chung JT, Lau CML & Chau Y. (2021). The effect of polysaccharide-based hydrogel on the response of antigen presenting cell line to immunomodulators. Biomaterials Science 9.19 (2021): 6542-6554.
- Chung CHY, Lau CML, Sin DT, Chung, JT, Zhang Y, Chau Y & Yao S. (2021). Droplet-Based Microfluidic Synthesis of Hydrogel Microparticles via Click Chemistry-Based Cross-Linking for the Controlled Release of Proteins. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 4(8), 6186-6194.
- Lau CML, Jahanmir G, Yu Y & Chau Y. (2021). Controllable multi-phase protein release from in-situ hydrolyzable hydrogel. Journal of Controlled Release, 335, 75-85.
- Jahanmir G, Lau CML, Abdekhodaie MJ & Chau, Y. (2020). Dual-Diffusivity Stochastic Model for Macromolecule Release from a Hydrogel. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 3(7), 4208-4219.
Powered By